What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?
 Information Architecture is a field and approach to designing clear, understandable communications by giving care to structure, context, and presentation of data and information. Particularly refers to websites and intranets, including labelling and navigation schemes. An information technology infrastructure however, is the base or foundation for the delivery of information to support programs and management (of an agency for example). The infrastructure contains elements upon which an agency's information technology activities are dependent. An agency must therefore define, implement, and manage these infrastructure elements to successfully employ information technology.
Information Architecture is a field and approach to designing clear, understandable communications by giving care to structure, context, and presentation of data and information. Particularly refers to websites and intranets, including labelling and navigation schemes. An information technology infrastructure however, is the base or foundation for the delivery of information to support programs and management (of an agency for example). The infrastructure contains elements upon which an agency's information technology activities are dependent. An agency must therefore define, implement, and manage these infrastructure elements to successfully employ information technology.Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture
Enterprise information architecture should focus on:
1. Backup and recovery
2. Disaster recovery
3. Information security
A single backup or restore failure can cost an organisation more than time and money; some data cannot be recreated, and the business intelligence lost from that data can be tremendous.
Chief information officers (CIO) should have enough confidence in their backup and recovery systems that they could walk around and randomly pull out cables to prove that the systems are safe. The CIO should also be secure enough to perform this test during peak business hours.
• A Hot Site - a separate and fully equipped facility where the company can move immediately after a disaster and resume business.
• A Cold Site - a separate facility that does not have any computer equipment, but is a place where employees can move after a disaster.
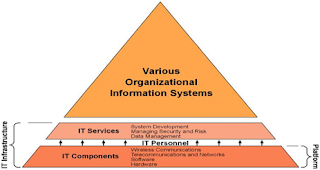
List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
Infrastructure architectures- includes the hardware, software and telecommunications equipment that, when combined provided the underlying foundation to support the organisation's goals
Five primary characteristics of solid infrastructure.
1. Reliability- ensuring all systems are functioning correctly and all information provided are correct
2. Scalability- how well a system can adapt to increased demands
3. Flexibility- systems must be flexible enough to meet all types of business changes
4. Availability- addressed when systems can be accessed by users
5. Performance- measures how quickly a system performs certain process or transaction
Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture
Service oriented architecture (SOA) is a business-driven IT architectural approach that supports integrating a business as linked, repeatable tasks or services.
SOA ensures that IT systems can adapt quickly, easily and economically to support rapidly changing business needs. Businesses can use existing applications, and re-use applications (services) many times for different tasks, making development cheaper and more flexible
Figure 5.9 The service oriented architecture
What is an event?
Event is an electronic message indicating that something has happened, it detect threats and opportunities and alerts those who can act on the information
What is a service?
Service contains a set of related commands that can be re-used, it is more like a software product than they are a coding project
What emerging technologies can companies can use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
Companies can use emerging technologies such as; Grid computing which connects different IT resources to coordinate them across a network, allowing them to function as a virtual whole to deliver improved performance, higher quality of service, better utilization and easier access to data.
- Improving productivity and collaboration of virtual organisations and respective computing and data resources. eBay is using grid computing to deliver online auction services to millions of users.
- Allowing widely dispersed departments and businesses to create virtual organisations to share data and resources for instantaneous, buyers of eBay have access to a range of goods and service that have being placed online to be sold.
-Building strong and infinitely flexible and resilient operational architectures
-Providing instantaneous access to massive computing and data resources
-Leveraging existing capital investments, which in turn help to ensure optimal utilization and costs of computing capabilities.














